This week is all about the latest addition to the ability to easily configure the Intune Management Extension as a managed installer on Windows devices. That addition is the ability to easily configure the Intune Management Extension as a managed installer for a specific group of Windows devices. Before it was already really easy to get started with the Intune Management Extension as a managed installer, but that was a tenant-wide configuration, meaning that it was immediately applicable to all Windows devices within the environment. And that now changed. That configuration can now be assigned to specific group of Windows devices. That assignment provides a lot more flexibility with introducing and testing the Intune Management Extension as managed installer. Eventually, that will make the introduction of App Control for Business a lot easier within organizations. This post will provide more details around that configuration and the impact on existing configurations, followed with the steps to easily take advantage of that configuration. This post will end with verifying the applied configuration on Windows devices.
Note: The focus of this post will be configuring the Intune Management Extension as managed installer and trusting those apps. Additional App Control for Business profiles will be for another blog post.
Configuring Intune Management Extension as managed installer
When looking at configuring the Intune Management Extension as managed installer and trusting its installations, it all starts with the general managed installer configurations in Microsoft Intune. Those configurations will make sure that applications that are installed via the Intune Management Extension are automatically tagged. And that tag will make sure that those applications are automatically identified by the App Control for Business policies as safe applications that can be allowed to run on the device. The following seven steps walk through the specifically targeted configuration for the managed installer.
- Open the Microsoft Intune admin center portal and navigate to Endpoint security > App Control for Business
- On the Endpoint security | App Control for Business page, on the Managed Installer tab, click Create
- On the Basics page, specify a valid name to distinguish the policy from other similar policies and click Next
- On the Settings page, as shown in Figure 1, switch the slider with Enable Intune Management Extension as Managed Installer to Enabled and click Next
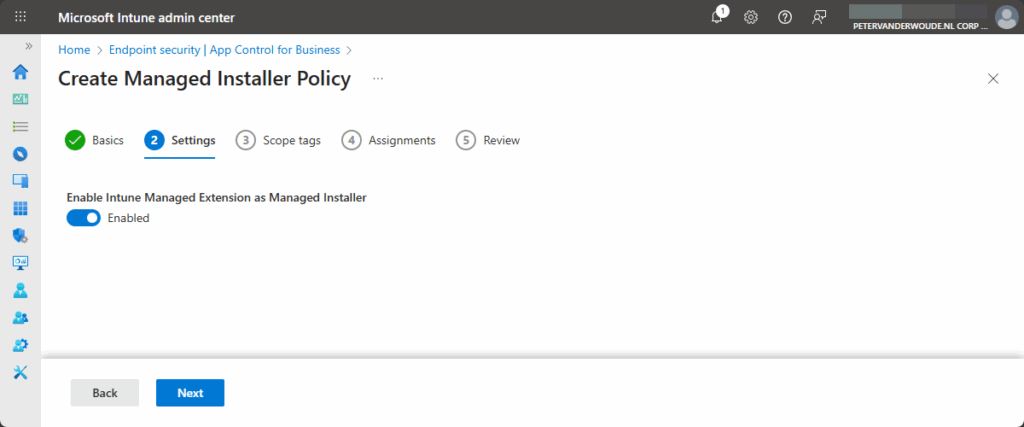
- On the Scope tags page, configure the required scope tags and click Next
- On the Assignments page, configure the required assignment by selecting the applicable group and click Next
- On the Review page, review the configuration and click Save
Note: When an existing managed installer configuration is already available, it will be shown as SideCar ManagedInstaller Script and it will be assigned to the default All devices group.
Configuring App Control for Business to automatically trust applications from managed installers
After making sure that the Intune Management Extension is configured as a managed installer, the next step is actually taking advantage of that. For that purpose, Microsoft Intune has the App Control for Business policies. Those policies rely on the ApplicationControl CSP and are available via the Endpoint security node within Microsoft Intune. And those policies can be used to easily manage which apps are allowed to run on the managed Windows devices. Any apps that aren’t explicitly allowed to run, are blocked from running. For testing purposes, these policies can also run in audit mode. With audit mode enabled in the policy, the policy allows all apps to run and logs the details in the Event Viewer.
Note: The ApplicationControl CSP was introduced in Windows to replace the AppLocker CSP. The AppLocker CSP is still supported, but Microsoft no longer adds new features and the improvements are in the ApplicationControl CSP.
Once the different configuration are known, it’s time to look at the actual configuration of an App Control for Business policy. As the focus for this post is on the ability to configure the Intune Management Extension as a managed installer, the following seven steps will walk through the configuration of an App Control for Business policy using the built-in controls.
- Open the Microsoft Intune admin center portal and navigate to Endpoint security > App Control for Business
- On the Endpoint security | Application control page, on the Application control tab, click Create Policy
- On the Basics page, specify a valid name to distinguish the policy from other similar policies and click Next
- On the Configuration settings page, as shown in Figure 2, provide the following information and click Next
- Policy creation type: Select Built-in controls to use the simplest path to configure a basic policy
- Audit mode: Switch to Enabled when using this policy for auditing purposes only
- Trust apps from managed installer: Switch to Enabled to allow devices to run the apps that were deployed by a managed installer. This includes apps that are deployed through Microsoft Intune after configuring the Intune Management Extension as a managed installer.
- Trust apps with good reputation: Switch to Enabled to allow devices to run reputable apps as defined by the Microsoft Intelligent Security Graph.
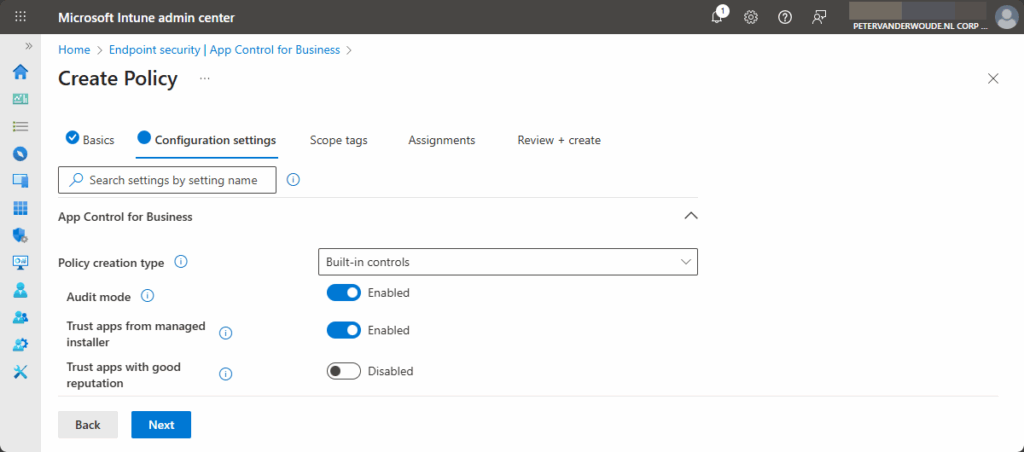
- On the Scope tags page, configure the required scope tags and click Next
- On the Assignments page, configure the required assignment by selecting the applicable group and click Next
- On the Review + create page, review the configuration and click Save
Note: With App Control for Business policies, it’s possible to easily create supplemental policies that add additional rules.
Experiencing Intune Management Extension as managed installer
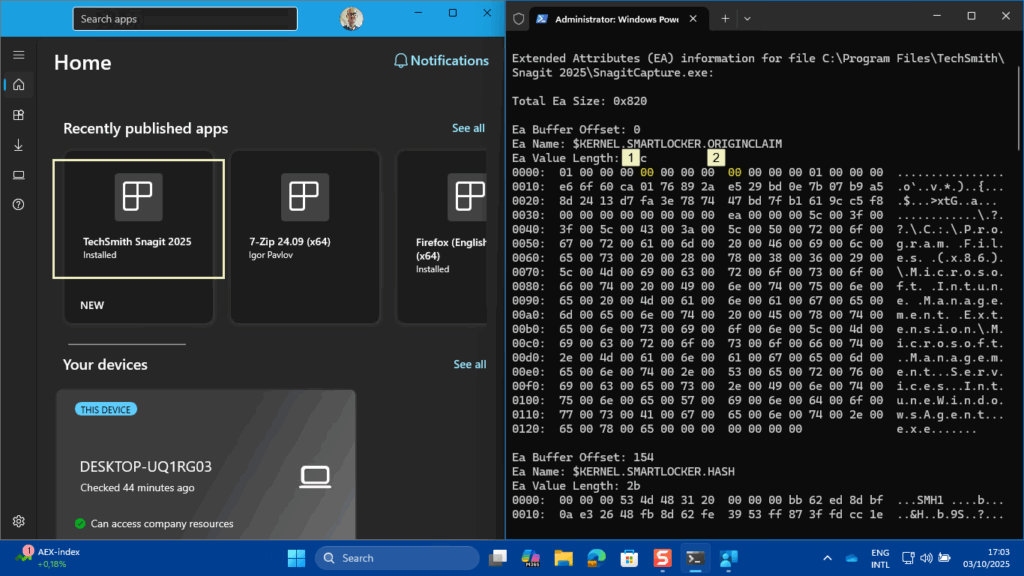
There are actually many different methods to verify the applied configuration. The most direct method is the method documented here by Microsoft. IT administrators can use fsutil.exe to determine whether a file was created by a managed installer process. That is exactly what the Intune Management Extension will be after applying the earlier mentioned configuration. So, when installing an app via Microsoft Intune, using the Intune Management Extension, the installed app will be tagged as being created by a managed installer process. That verification can be done by actually querying extended attributes on a file using fsutil.exe. As a starting point, below on the left in Figure 3, is the successful installation of Snagit 2025.
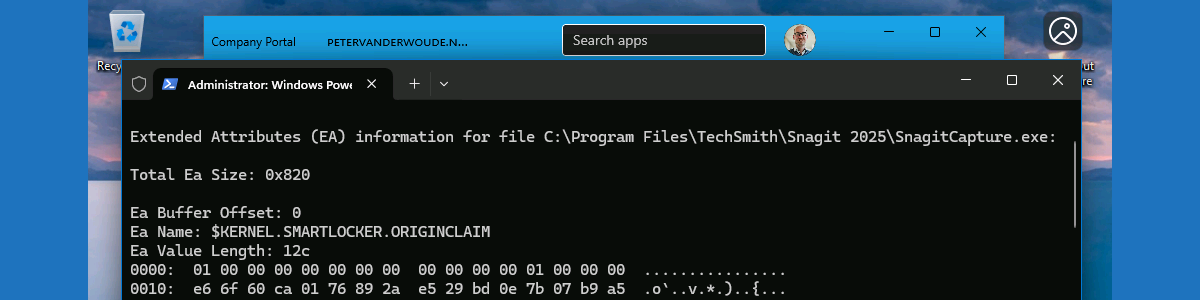
When using the command for Snagit 2025, as shown below on the right in Figure 3, look for the extended attribute of KERNEL.SMARTLOCKER.ORIGINCLAIM. The confirmation can be found in the first row of data labeled with 0000. The 00 in the fifth position (shown with number 1) of the output indicates that the extended attribute is related to managed installer. The 00 in the ninth position (shown with number 2) of the output indicates that the file was directly written by a managed installer process and will run if the App Control for Business policy trusts managed installers.
More information
For more information about Application Control for Business and managed installers, refer to the following docs.
- Manage approved apps for Windows devices with App Control for Business policy and Managed Installers in Microsoft Intune – Microsoft Intune | Microsoft Learn
- Managed installer and ISG technical reference and troubleshooting guide | Microsoft Learn
- Allow apps deployed with an App Control managed installer | Microsoft Learn
- Application Control for Windows | Microsoft Learn
Discover more from All about Microsoft Intune
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.

1 thought on “Easily getting started with Intune Management Extension as managed installer”