This week is all about browser extensions. And more specifically, about Microsoft Edge browser extension on Windows devices. There are many reasons why organizations might want to look into managing and controlling Microsoft Edge browser extensions. Most of those reasons, however, are security related and focussed on staying in control of corporate data. Lately, there have been multiple examples of malicious browser extensions – not specific to the Microsoft Edge browser – that would collect user data and exfiltrate it to a malicious website. A good reason to get in control of the browser extensions that are being used within the organization. Either by fully controlling which browser extensions can be installed, or by at least blocking unwanted browser extensions. This post will look specifically at managing extensions for Microsoft Edge. Starting with the search towards the required extensions, directly followed with the main configuration options, and ending with the experience.
Note: Microsoft Defender Vulnerability Management contains a browser extensions assessment that can be used to determine the risk of browser extensions in Microsoft Edge, Google Chrome, and Mozilla Firefox.
Determining which browser extensions to install
When looking at managing Microsoft Edge browser extensions, it all starts with determining which browser extensions to install. Nowadays, a big part of a working day takes place in the browser of the user. Many apps that are only available via the browser, keeping the user there for a long time. That also makes the browser the go-to location for the user. So, the easier it can get within the browser, the better the experience for the user. And that’s where the organization should get careful. There should always be a fine balance between usability/productivity and security. In the end it’s important to protect the corporate data.
For protecting corporate data, it’s important to be familiar with the regulations and compliance measures to adhere to, the permissions that are required, and the corporate data stored on the device. After being familiar with that information, it’s important to translate that to the best approach for the organization. That starts with determining whether to block or allow specific browser extensions. When allowing browser extensions, the next step is to determine whether to force install specific extensions, followed with determining whether to implement a block or allow list for browser extensions.
In the early days of managing Microsoft Edge browser extensions, it was always focused on using a block or an allow list for browser extensions. Nowadays, there is an in-between model that enables IT administrators to manage the permissions requested by browser extensions. That provides more flexibility and granularity.
Configuring allowed Microsoft Edge browser extensions
After determining which Microsoft Edge browser extensions to install, it’s time to look at configuring those extensions. The most common settings used for managing browser extensions are ExtensionInstallAllowlist, ExtensionInstallBlocklist, and ExtensionInstallForcelist. Those settings can be used for creating a list of allowed browser extensions, a list of blocked browser extensions, and a list of browser extension that are forced installed. By using Microsoft Intune, those settings can be managed via the Settings Catalog. The following 8 steps can be used to configure an allow list for browser extensions, by using Settings Catalog, to block all browser extensions and only allow specifically allowed browser extensions.
- Open the Microsoft Intune admin center portal and navigate to Devices > Windows > Configuration profiles
- On the Windows | Configuration profiles blade, click Create > New Policy
- On the Create a profile blade, select Windows 10 and later > Settings catalog and click Create
- On the Basics page, provide at least a unique name to distinguish it from similar profiles and click Next
- On the Configuration settings page, as shown below in Figure 1, perform the following actions and click Next
- Click Add settings, navigate to Microsoft Edge > Extensions and select the following settings in Settings picker
- Control which extensions cannot be installed (ExtensionInstallBlocklist)
- Allow specific extensions to be installed (ExtensionInstallAllowlist)
- Configure the following values for the different settings
- Switch Control which extensions cannot be installed to Enabled (1) and specify * with Extension IDs the user should be prevented from installing (or * for all) (Device) to block all browser extensions
- Switch Allow specific extensions to be installed to Enabled (2) and specify the allowed Extenion IDs with Extension IDs to exempt from the block list (Device) to allow only those extensions

- On the Scope tags page, configure the required scope tags and click Next
- On the Assignments page, configure the assignment for the required user or devices and click Next
- On the Review + create page, verify the configuration and click Create
Note: For more detailed configuration capabilities for browser extensions the ExtensionSettings policy can be used.
Experiencing allowed Microsoft Edge browser extensions
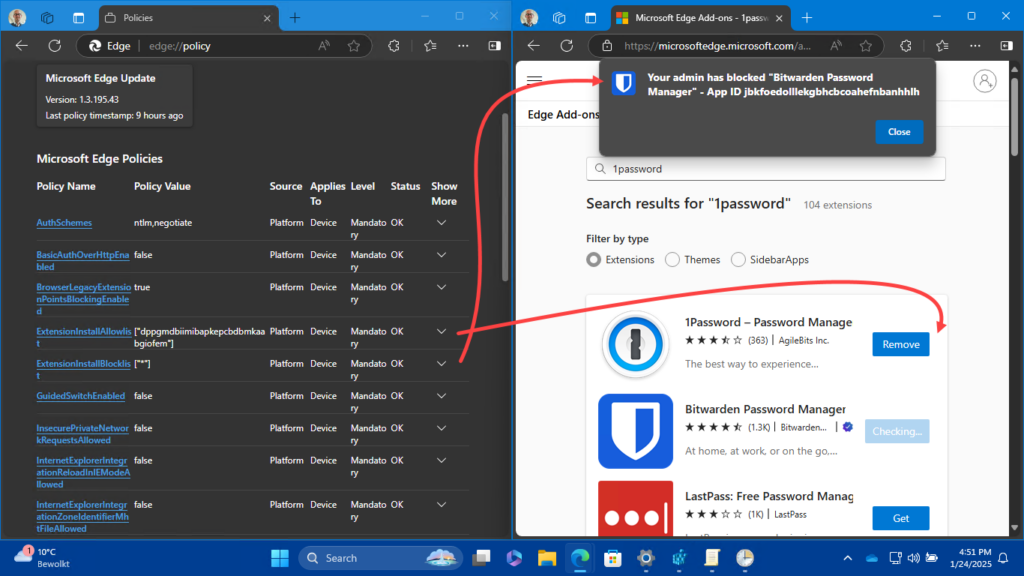
When the configuration for the allowed browser extensions is in place, it’s time to look at the user experience. And that experience is pretty straight forward to verify by simply trying to install different browser extensions. Below in Figure 2 is an overview of what happens when all browser extensions are blocked in Microsoft Edge and only one specific extension is allowed. The configuration for Microsoft Edge is shown on the left and that indicates that all browser extensions are block, with the exception of 1Password. That configuration results into the behavior shown on the right. The 1Password browser extension can be installed, and any other browser extension, like for example Bitwarden Password Manager, or LastPass, will be blocked.
More information
For more information about managing Microsoft Edge browser extensions, refer to the following docs.
- Browser extensions assessment – Microsoft Defender Vulnerability Management | Microsoft Learn
- Manage Microsoft Edge extensions in the enterprise | Microsoft Learn
- Deploy Microsoft Edge policy using ADMX template in Microsoft Intune | Microsoft Learn
Discover more from All about Microsoft Intune
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.

Where and how can you get an Extenion IDs for the allow list?
Thank you.
Hi Mike,
You can find the ID in the browser when you select the extension.
Regards, Peter
Please share the steps on How to uninstall an extension ?
Hi Raj,
Not sure if you can do something like that. You can block the installation, but that won’t uninstall it.
Regards, Peter